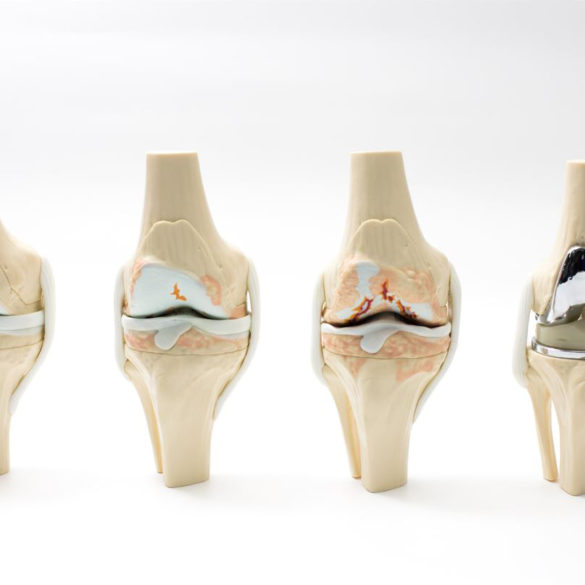
The most prevalent chronic joint ailment is osteoarthritis (OA).
A joint is where two bones meet. The tissue that protects the ends of the bones is called cartilage. This cartilage deteriorates in OA, which causes the bones in the joint to rub against one another. Pain, stiffness, and other symptoms may result from this.
In every joint, OA can happen. However, the bodily parts that are most frequentlyaffected are the:
- Hands
- Fingers
- Shoulder
- At the neck or lower back
- Hips
- Knees
OA is a leading cause of disability worldwide, with age being one of the primary causes of the joint damage that results in OA as this damage can accumulate over time. Your joints are subjected to increasing repeated stress as you age.

What Puts You At Risk of OA ?
Your likelihood of having OA can also be increased by the following:
- Having relatives with the illness, especially parents or siblings
- Gender, with a greater prevalence of OA in women than in males
- Being 50 years or older
- After menopause
- Having a job that requires bending down, climbing, moving big objects, or comparable tasks
- Having a different form of arthritis or diabetes that has an impact on your ability to move freely. Your chance of acquiring OA in other body parts rises if you already have OA in one area of your body.
- Having a weight problem, having obesity, or being overweight
- A history of injury. Injuries to the joints can also result from:
- Previous injuries such as dislocated joints, damaged ligaments, or torn cartilage
- Joint deformity
- Improper posture

Treatment for Osteoarthritis
The main focus of OA therapy is symptom control. The extent and location of your symptoms will determine the sort of treatment that will benefit you the best.Most of the time, over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, lifestyle modifications, and home remedies will be sufficient to relieve your pain, stiffness, and swelling.
The Effects of Osteoarthritis
Physical effects from arthritis, particularly OA, are widely established. Additionally, OA might lead to other health problems including:
- Sleep deprivation
- Weight increase brought on by discomfort or restricted movement
- Bone death, or osteonecrosis
- Erosion of the tendons and ligaments
- Stress fractures along the hairline
- Hemarthrosis, often known as bleeding around the joints
- Anxiety and stress brought on by the loss of function
Prevention of Osteoarthritis
You could be born with OA risk factors, such as heredity and age, but there are also several risk factors that can be manageable. These can assist in lowering your risk.
- Be careful to take care of your body if you participate in sports or exercise frequently.
- Put on supportive athletic footwear.
- Try to use all of your muscles, not just the same ones every time, be sure to mix up your exercises.
- Sustain a healthy weight. Maintain an optimal body mass index for your height and sex.
- Consume a healthy diet. Choose a variety of healthful foods with an emphasis on fruits and vegetables.
- Take time to rest. Ensure that your body has enough relaxation and sleep.
- Monitor your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
Do not disregard signs of persistent stiffness and joint discomfort. Your chances of receiving a diagnosis, starting treatment, and enhancing your quality of life increase the sooner you talk with a doctor.

Disclaimer
BahrainHealthMatters.com is for informative purposes only and not a substitute for professional in person expertise.
We advise that anyone having concerns about their health issues should consult their doctor asap.